Hyperbolic metamaterials (HMM) based on ordered arrays of metal nanorods in a dielectric matrix are extremely attractive optical materials for manipulating the parameters of light [1]. One of the most promising tools for in situ tuning the optical properties of metamaterials is the application of an external magnetic field [2]. However, for the case of HMM based on the ordered arrays of magneto-plasmonic nanostructures, this effect has not been clearly demonstrated yet.
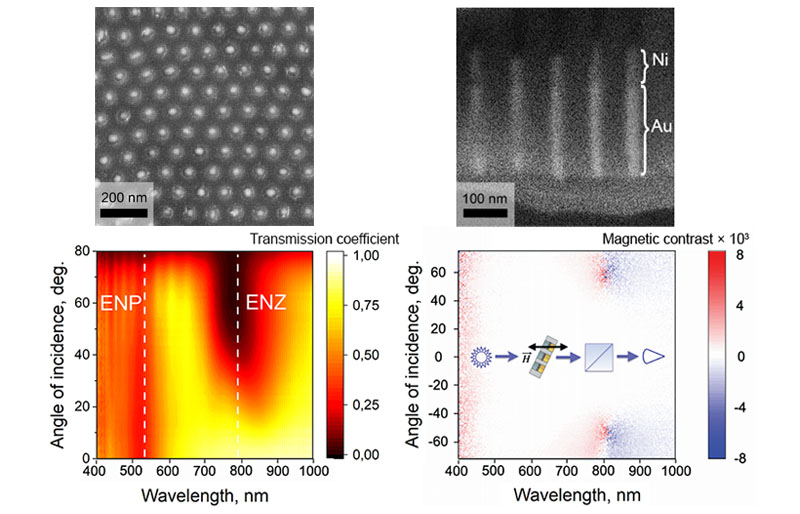
In a recent paper [3], we present the results on the synthesis of HMM based on the highly-ordered arrays of bisegmented Au/Ni nanorods in porous anodic alumina templates and a detailed study of their optical and magneto-optical properties. Distinct enhancement of magnetic contrast along with its sign reversal is observed in the spectral vicinity of the pole and zero value of dielectric permeability. For example, in the Faraday geometry when the beam passes first through the Ni segments and then through the gold ones magnetic contrast reaches the values of 6·103 at the wavelength of 800 nm and the angle of incidence of ~55°. After the p-polarized light passes through the Ni layer, its polarization plane rotates due to the nickel gyrotropy and is slightly inclined with respect to the plane of incidence. The Au layer screws it up due to the absorption anisotropy as well as due to the difference between the phase velocities of the ordinary and extraordinary beams. The results look promising for nanophotonics devices and magnetic-field-controllable light manipulation.
This work was supported by Russian Science Foundation (grant № 18-73-10151).
[1] M.G. Silveirinha, Nonlocal homogenization model for a periodic array of epsilon-negative rods // Physical Review E, 2006, v. 73, 10. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.73.046612.
[2] A.K. Zvezdin, V.A. Kotov, Modern Magnetooptics and Magnetooptical Materials // Taylor & Francis, 1997.
[3] I.V. Malysheva, I.A. Kolmychek, A.M. Romashkina, A.P. Leontiev, K.S. Napolskii, T.V. Murzina, Magneto-optical effects in hyperbolic metamaterials based on ordered arrays of bisegmented gold/nickel nanorods // Nanotechnology, 2021, v. 32, 305710. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/abf691.